Important: The GCConnex decommission will not affect GCCollab or GCWiki. Thank you and happy collaborating!
Difference between revisions of "CNSC Laboratory ISO 17025 Accreditation"
m |
m |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[File:CNSC ISO Banner.png|center|thumb|1200x1200px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <br /> | |
| + | <!--This is the code for the tab table--> | ||
| + | <!--In order to add another "tab", copy the code from the exclamation mark until the </div>--> | ||
| + | <big> | ||
| + | {| width="100%" class="FCK__ShowTableBorders" style="border: 4px solid DarkSlateBlue; background-color:DarkCyan; border-image: none;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! width="20%" height="50" scope="col" | <div style="text-align: center;"> [[CNSC_Laboratory_ISO_17025_Accreditation|<span style="color: Snow"> Home]]</div> | ||
| + | ! width="20%" height="50" scope="col" | <div style="text-align: center;"> [[Quality_Policy (CNSC_Laboratory_Calibration_Services)|<span style="color: Snow"> Quality Policy & Statement]]</div> | ||
| + | ! width="40%" height="50" scope="col" | <div style="text-align: center;"> [[Customer_Satisfaction_Survey_Results|<span style="color: Snow"> Customer Satisfaction Survey Results]]</div> | ||
| + | ! width="20%" height="50" scope="col" | <div style="text-align: center;"> [[At_Your_Service|<span style="color: Snow"> At Your Service ]]</div> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | On November 16, 2016, the CNSC laboratory was granted accreditation to [https://www.iso.org/standard/39883.html ISO/IEC 17025:2005], a standard used throughout the world to evaluate testing and calibration laboratories. The accreditation scope includes the calibration of working measurement standards, gamma survey meters, and personal electronic dosimeters – in short, a significant part of the CNSC laboratory’s calibration services. | + | '''<big>Author: Aslam Ibrahim</big>''' |
| − | Accreditation was granted by the Standards Council of Canada (SCC), under the Program for the Accreditation of Laboratories – Canada (PALCAN) and the National Research Council of Canada Calibration Laboratory Assessment Service (NRC CLAS). | + | |
| − | It is notable that the CNSC laboratory is the first of its kind | + | On November 16, 2016, the [https://www.nuclearsafety.gc.ca/eng/resources/cnsc-laboratory/index.cfm CNSC laboratory] was granted accreditation to [https://www.iso.org/standard/39883.html ISO/IEC 17025:2005], a standard used throughout the world to evaluate testing and calibration laboratories.<ref>https://cala.ca/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/ilac_why_become_accred_lab.pdf</ref><ref>https://ilac.org/about-ilac/</ref><ref>https://www.scc.ca/en/accreditation/programs/laboratories#:~:text=The%20Standards%20Council%20of%20Canada%20%28SCC%29%20offers%20internationally,for%20the%20competence%20of%20testing%20and%20calibration%20laboratories.</ref><ref>https://nrc.canada.ca/en/certifications-evaluations-standards/calibration-laboratory-assessment-service/about-calibration-laboratory-assessment-service</ref> The [https://nrc.canada.ca/en/certifications-evaluations-standards/calibration-laboratory-assessment-service/directory-accredited-calibration-laboratories/clas-certificate-number-2016-05 accreditation scope] includes the calibration of [[wikipedia:Standard_(metrology)#:~:text=In metrology (the science of measurement), a standard,against which all other measuring devices are compared.|working measurement standards]], [https://www.nuclear-power.net/nuclear-engineering/radiation-dosimetry/radiation-dosimeter/dosimetry-in-nuclear-power-plants/portable-survey-meters-gamma-survey-meter/ gamma survey meters], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_personal_dosimeter personal electronic dosimeters] – in short, a significant part of the CNSC laboratory’s calibration services. |
| + | Accreditation was granted by the Standards Council of Canada [https://www.scc.ca/en/accreditation/programs/laboratories#:~:text=The%20Standards%20Council%20of%20Canada%20%28SCC%29%20offers%20internationally,for%20the%20competence%20of%20testing%20and%20calibration%20laboratories. (SCC)], under the Program for the Accreditation of Laboratories – Canada [https://www.scc.ca/en/agl-palcan (PALCAN)] and the National Research Council of Canada Calibration Laboratory Assessment Service [https://nrc.canada.ca/en/certifications-evaluations-standards/calibration-laboratory-assessment-service/about-calibration-laboratory-assessment-service (NRC CLAS)]. | ||
| + | It is notable that the CNSC laboratory is the first of its kind In Canada that the SCC has accredited for calibration of working measurement standards and survey instruments for gamma measurement. | ||
For the purposes of this article, the term “working measurement standard” refers to a measuring instrument that is calibrated relative to a reference measurement standard (which is also a measuring instrument). The working and reference measurement standards each consist of an ion chamber and an electrometer that are combined as a single measurement system. | For the purposes of this article, the term “working measurement standard” refers to a measuring instrument that is calibrated relative to a reference measurement standard (which is also a measuring instrument). The working and reference measurement standards each consist of an ion chamber and an electrometer that are combined as a single measurement system. | ||
The laboratory maintains the reference measurement standard through annual calibrations that are performed by the [https://nrc.canada.ca/en/certifications-evaluations-standards/instrument-calibration-services/ionizing-radiation-standards-calibration-services NRC]. The laboratory then calibrates the working measurement standard in-house by directly comparing it to the (calibrated) reference measurement standard. The calibration of the working measurement standards has also been accredited by SCC and NRC CLAS. | The laboratory maintains the reference measurement standard through annual calibrations that are performed by the [https://nrc.canada.ca/en/certifications-evaluations-standards/instrument-calibration-services/ionizing-radiation-standards-calibration-services NRC]. The laboratory then calibrates the working measurement standard in-house by directly comparing it to the (calibrated) reference measurement standard. The calibration of the working measurement standards has also been accredited by SCC and NRC CLAS. | ||
| − | + | === '''What is accreditation and why is it important?''' === | |
| − | Laboratory accreditation is a formal process of recognition by a third party organization to establish that a laboratory is technically competent and impartial. The CNSC laboratory was required to demonstrate its ability to produce precise and accurate test and calibration data, and to show the technical competence of staff. Learn more. | + | [[File:Certificate.png|thumb|Certificate of accreditation for CNSC laboratory issued by SCC and NRC CLAS|left|600x600px]] |
| + | Laboratory accreditation is a formal process of recognition by a third party organization to establish that a laboratory is technically competent and impartial. The CNSC laboratory was required to demonstrate its ability to produce precise and accurate test and calibration data, and to show the technical competence of staff. [https://ilac.org/publications-and-resources/ilac-promotional-brochures/ Learn more]. | ||
| − | One reason that the CNSC pursued this recognition for the laboratory is because | + | One reason that the CNSC pursued this recognition for the laboratory is because ISO/IEC 17025:2005 is an internationally accepted standard. Accreditation to such a standard provides formal recognition of competent laboratories throughout the world. |
This recognition is important because, in all its efforts to fulfill its mandate, the CNSC strives continuously not only to achieve excellence in its operations, but also to foster public trust and confidence. The CNSC laboratory is no exception. With the calibration services becoming accredited by recognized bodies like the SCC and NRC CLAS, the CNSC laboratory has received a significant global mark of approval of high quality of its services. This in turn contributes to building public trust and confidence in the laboratory’s operations and the CNSC as a whole. | This recognition is important because, in all its efforts to fulfill its mandate, the CNSC strives continuously not only to achieve excellence in its operations, but also to foster public trust and confidence. The CNSC laboratory is no exception. With the calibration services becoming accredited by recognized bodies like the SCC and NRC CLAS, the CNSC laboratory has received a significant global mark of approval of high quality of its services. This in turn contributes to building public trust and confidence in the laboratory’s operations and the CNSC as a whole. | ||
| − | + | === '''What did the accreditation process involve?''' === | |
During this voluntary process, specialist technical assessors from NRC CLAS and NRC Measurement Science and Standards first conducted a thorough desktop assessment of the management system manual documentation and then a rigorous onsite evaluation of the laboratory’s processes, staff and equipment. | During this voluntary process, specialist technical assessors from NRC CLAS and NRC Measurement Science and Standards first conducted a thorough desktop assessment of the management system manual documentation and then a rigorous onsite evaluation of the laboratory’s processes, staff and equipment. | ||
| − | Upon concluding that the CNSC Laboratory met all requirements of the stringent | + | Upon concluding that the CNSC Laboratory met all requirements of the stringent ISO/IEC 17025:2005 standard, NRC CLAS recommended accreditation to the SCC, which reviewed the results of assessment and granted the recognition. |
| − | + | === '''How do CNSC staff members (customers) and licensees benefit?''' === | |
The results of the process showcase the technical and service-oriented capabilities of the CNSC laboratory, including highly professional technical staff, equipment, processes, and successful participation in proficiency testing. Together these features make the laboratory a leader in calibration services that are crucial for reliable radiation measurements – a key component of nuclear regulation. | The results of the process showcase the technical and service-oriented capabilities of the CNSC laboratory, including highly professional technical staff, equipment, processes, and successful participation in proficiency testing. Together these features make the laboratory a leader in calibration services that are crucial for reliable radiation measurements – a key component of nuclear regulation. | ||
| − | The | + | The ISO/IEC 17025:2005 accreditation provides high confidence to both the regulator and licensees in the data used for key analyses and regulatory decisions. |
| − | + | === '''What were the challenges the laboratory faced while preparing for accreditation?''' === | |
| − | Adapting all in-house MS Excel spreadsheets, writing procedures and work instructions to comply with all the | + | Adapting all in-house MS Excel spreadsheets, writing procedures and work instructions to comply with all the ISO/IEC 17025:2005 standard requirements was certainly a big challenge. There are a lot of documents! |
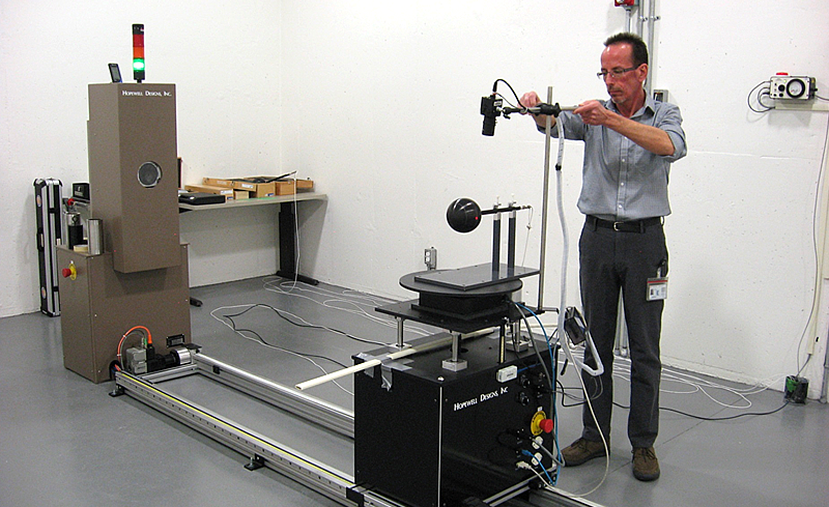
| + | [[File:Clifford.png|thumb|Instrumentation Technologist Clifford Chouinor sets up working standard for calibration at the CNSC laboratory|400x400px]] | ||
Another significant challenge was to find proficiency testing (PT) providers with appropriate measurement capabilities to meet ISO compliance requirements. The capabilities of the few established and reputable PT providers, such as the National Research Council of Canada (NRC), the National Institute of Standards and Technologies (NIST) and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), are limited to their well-characterized artefacts consisting of working measurement instruments for air kerma measurements. Their PT capabilities do not extend to field instruments such as personal dosimeters and gamma survey equipment. | Another significant challenge was to find proficiency testing (PT) providers with appropriate measurement capabilities to meet ISO compliance requirements. The capabilities of the few established and reputable PT providers, such as the National Research Council of Canada (NRC), the National Institute of Standards and Technologies (NIST) and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), are limited to their well-characterized artefacts consisting of working measurement instruments for air kerma measurements. Their PT capabilities do not extend to field instruments such as personal dosimeters and gamma survey equipment. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 48: | ||
It is important to note that the accreditation task presented to the Standards Council of Canada (SCC) and NRC CLAS, with the measurement scope that the CNSC laboratory sought, was the first of its kind for all three of these primary project stakeholders, and a first for Canada. The unique scope of accreditation turned out to be a challenge for the SCC and the NRC Calibration Laboratory Assessment Service (NRC CLAS), as the requirements for the analysis of measurement uncertainties and model equations, in addition to data analysis of the measurements and interpretation of the comparison of results from PT exercises are different from other physical and electrical metrological calibrations. | It is important to note that the accreditation task presented to the Standards Council of Canada (SCC) and NRC CLAS, with the measurement scope that the CNSC laboratory sought, was the first of its kind for all three of these primary project stakeholders, and a first for Canada. The unique scope of accreditation turned out to be a challenge for the SCC and the NRC Calibration Laboratory Assessment Service (NRC CLAS), as the requirements for the analysis of measurement uncertainties and model equations, in addition to data analysis of the measurements and interpretation of the comparison of results from PT exercises are different from other physical and electrical metrological calibrations. | ||
| − | + | === '''What’s next?''' === | |
| − | The current scope of accreditation includes working measurement standards for air kerma measurements, gamma survey meters, and personal electronic dosimeters. The CNSC laboratory has prepared a project management plan to extend the scope to include electronic and radiological calibrations of survey meters for gamma, neutron, alpha and beta radiation measurements, as well as energy calibrations of the spectrometers used for gamma and neutron measurements. There’s lots more to do! | + | The current scope of accreditation includes working measurement standards for air kerma measurements, gamma survey meters, and personal electronic dosimeters. The CNSC laboratory has prepared a project management plan to extend the scope to include electronic and radiological calibrations of survey meters for gamma, neutron, alpha and beta radiation measurements, as well as energy calibrations of the spectrometers used for gamma and neutron measurements. There’s lots more to do! [[File:Typical_equipment.png|thumb|Typical instruments that the CNSC laboratory calibrates under the scope of accreditation|400x400px]] |
| − | + | === '''How can CNSC staff members suggest improvements to the laboratory?''' === | |
| − | |||
Through annual customer satisfaction surveys that the CNSC laboratory conducts, CNSC staff members who have used the laboratory services in the previous year can provide feedback on their quality, including suggestions for improvement. The CNSC laboratory has been conducting such surveys since 2015, and has taken action to address comments from its customers to meet its commitment to provide a high service level and meet customer expectations. One such action was to respond to the suggestion to provide links to instrument manuals from the laboratory’s Web page. | Through annual customer satisfaction surveys that the CNSC laboratory conducts, CNSC staff members who have used the laboratory services in the previous year can provide feedback on their quality, including suggestions for improvement. The CNSC laboratory has been conducting such surveys since 2015, and has taken action to address comments from its customers to meet its commitment to provide a high service level and meet customer expectations. One such action was to respond to the suggestion to provide links to instrument manuals from the laboratory’s Web page. | ||
The CNSC laboratory gamma calibration service now operates within a quality management system that complies with the requirements of [https://www.iso.org/standard/39883.html ISO/IEC 17025:2005]. As specified in the quality management system, the laboratory implements mechanisms including, but not limited to, proficiency testing, customer satisfaction surveys, internal reviews, management reviews, and corrective and preventative actions to drive continual improvement, which is the true intention of the ISO/IEC standard. | The CNSC laboratory gamma calibration service now operates within a quality management system that complies with the requirements of [https://www.iso.org/standard/39883.html ISO/IEC 17025:2005]. As specified in the quality management system, the laboratory implements mechanisms including, but not limited to, proficiency testing, customer satisfaction surveys, internal reviews, management reviews, and corrective and preventative actions to drive continual improvement, which is the true intention of the ISO/IEC standard. | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:52, 6 January 2021
Author: Aslam Ibrahim
On November 16, 2016, the CNSC laboratory was granted accreditation to ISO/IEC 17025:2005, a standard used throughout the world to evaluate testing and calibration laboratories.[1][2][3][4] The accreditation scope includes the calibration of working measurement standards, gamma survey meters, and personal electronic dosimeters – in short, a significant part of the CNSC laboratory’s calibration services. Accreditation was granted by the Standards Council of Canada (SCC), under the Program for the Accreditation of Laboratories – Canada (PALCAN) and the National Research Council of Canada Calibration Laboratory Assessment Service (NRC CLAS). It is notable that the CNSC laboratory is the first of its kind In Canada that the SCC has accredited for calibration of working measurement standards and survey instruments for gamma measurement. For the purposes of this article, the term “working measurement standard” refers to a measuring instrument that is calibrated relative to a reference measurement standard (which is also a measuring instrument). The working and reference measurement standards each consist of an ion chamber and an electrometer that are combined as a single measurement system.
The laboratory maintains the reference measurement standard through annual calibrations that are performed by the NRC. The laboratory then calibrates the working measurement standard in-house by directly comparing it to the (calibrated) reference measurement standard. The calibration of the working measurement standards has also been accredited by SCC and NRC CLAS.
What is accreditation and why is it important?
Laboratory accreditation is a formal process of recognition by a third party organization to establish that a laboratory is technically competent and impartial. The CNSC laboratory was required to demonstrate its ability to produce precise and accurate test and calibration data, and to show the technical competence of staff. Learn more.
One reason that the CNSC pursued this recognition for the laboratory is because ISO/IEC 17025:2005 is an internationally accepted standard. Accreditation to such a standard provides formal recognition of competent laboratories throughout the world.
This recognition is important because, in all its efforts to fulfill its mandate, the CNSC strives continuously not only to achieve excellence in its operations, but also to foster public trust and confidence. The CNSC laboratory is no exception. With the calibration services becoming accredited by recognized bodies like the SCC and NRC CLAS, the CNSC laboratory has received a significant global mark of approval of high quality of its services. This in turn contributes to building public trust and confidence in the laboratory’s operations and the CNSC as a whole.
What did the accreditation process involve?
During this voluntary process, specialist technical assessors from NRC CLAS and NRC Measurement Science and Standards first conducted a thorough desktop assessment of the management system manual documentation and then a rigorous onsite evaluation of the laboratory’s processes, staff and equipment.
Upon concluding that the CNSC Laboratory met all requirements of the stringent ISO/IEC 17025:2005 standard, NRC CLAS recommended accreditation to the SCC, which reviewed the results of assessment and granted the recognition.
How do CNSC staff members (customers) and licensees benefit?
The results of the process showcase the technical and service-oriented capabilities of the CNSC laboratory, including highly professional technical staff, equipment, processes, and successful participation in proficiency testing. Together these features make the laboratory a leader in calibration services that are crucial for reliable radiation measurements – a key component of nuclear regulation.
The ISO/IEC 17025:2005 accreditation provides high confidence to both the regulator and licensees in the data used for key analyses and regulatory decisions.
What were the challenges the laboratory faced while preparing for accreditation?
Adapting all in-house MS Excel spreadsheets, writing procedures and work instructions to comply with all the ISO/IEC 17025:2005 standard requirements was certainly a big challenge. There are a lot of documents!
Another significant challenge was to find proficiency testing (PT) providers with appropriate measurement capabilities to meet ISO compliance requirements. The capabilities of the few established and reputable PT providers, such as the National Research Council of Canada (NRC), the National Institute of Standards and Technologies (NIST) and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), are limited to their well-characterized artefacts consisting of working measurement instruments for air kerma measurements. Their PT capabilities do not extend to field instruments such as personal dosimeters and gamma survey equipment.
It is important to note that the accreditation task presented to the Standards Council of Canada (SCC) and NRC CLAS, with the measurement scope that the CNSC laboratory sought, was the first of its kind for all three of these primary project stakeholders, and a first for Canada. The unique scope of accreditation turned out to be a challenge for the SCC and the NRC Calibration Laboratory Assessment Service (NRC CLAS), as the requirements for the analysis of measurement uncertainties and model equations, in addition to data analysis of the measurements and interpretation of the comparison of results from PT exercises are different from other physical and electrical metrological calibrations.
What’s next?
The current scope of accreditation includes working measurement standards for air kerma measurements, gamma survey meters, and personal electronic dosimeters. The CNSC laboratory has prepared a project management plan to extend the scope to include electronic and radiological calibrations of survey meters for gamma, neutron, alpha and beta radiation measurements, as well as energy calibrations of the spectrometers used for gamma and neutron measurements. There’s lots more to do!
How can CNSC staff members suggest improvements to the laboratory?
Through annual customer satisfaction surveys that the CNSC laboratory conducts, CNSC staff members who have used the laboratory services in the previous year can provide feedback on their quality, including suggestions for improvement. The CNSC laboratory has been conducting such surveys since 2015, and has taken action to address comments from its customers to meet its commitment to provide a high service level and meet customer expectations. One such action was to respond to the suggestion to provide links to instrument manuals from the laboratory’s Web page.
The CNSC laboratory gamma calibration service now operates within a quality management system that complies with the requirements of ISO/IEC 17025:2005. As specified in the quality management system, the laboratory implements mechanisms including, but not limited to, proficiency testing, customer satisfaction surveys, internal reviews, management reviews, and corrective and preventative actions to drive continual improvement, which is the true intention of the ISO/IEC standard.
- ↑ https://cala.ca/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/ilac_why_become_accred_lab.pdf
- ↑ https://ilac.org/about-ilac/
- ↑ https://www.scc.ca/en/accreditation/programs/laboratories#:~:text=The%20Standards%20Council%20of%20Canada%20%28SCC%29%20offers%20internationally,for%20the%20competence%20of%20testing%20and%20calibration%20laboratories.
- ↑ https://nrc.canada.ca/en/certifications-evaluations-standards/calibration-laboratory-assessment-service/about-calibration-laboratory-assessment-service