Important: The GCConnex decommission will not affect GCCollab or GCWiki. Thank you and happy collaborating!
Difference between revisions of "Guidance"
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Cloud Information Centre - Government of Canada}} | {{Cloud Information Centre - Government of Canada}} | ||
| − | *** | + | <b> |
| + | </b> | ||
| + | <!-- Columns --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| width="100%" cellpadding="10" | ||
| + | |-valign="top" | ||
| + | |||
| + | |width="50%" style="color: black;" | | ||
| + | <!-- COLUMN 1 STARTS: --> | ||
| + | [[Image:Governance.jpg|250x250px|center |link=Governance]] | ||
| + | <!-- COLUMN 1 ENDS: --> | ||
| + | |width="50%" style="color: black;" | | ||
| + | <!-- COLUMN 2 STARTS: --> | ||
| + | [[Image:Cic.jpg|center|250x250px |link=GC_Cloud_Infocentre]] | ||
| + | <!-- COLUMN 2 ENDS: --> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <span style="font-family: Century Gothic; font-size: 28pt;"><font color="#9F000F;">Guidance</font></span> | ||
| + | <big><big> | ||
| + | == Overview == | ||
| + | The GC Cloud first strategy indicates that when evaluating new IT investments, initiatives, strategies and projects, Departments should consider Cloud options first. | ||
| + | Learn more about the Cloud first strategy by clicking [https://www.canada.ca/en/government/system/digital-government/modern-emerging-technologies/cloud-services/gc-white-paper-data-sovereignty-public-cloud.html here]. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | == What is the Cloud?== | ||
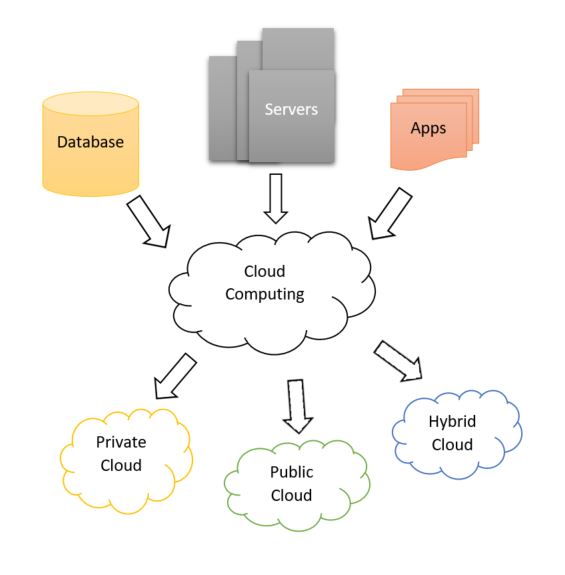
| + | Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing resources (from applications to data centres) over the Internet on a pay-for-use basis | ||
| + | [[File:Cloud computing.jpg|800px |frameless|center]] | ||
| + | ==Cloud deployment models == | ||
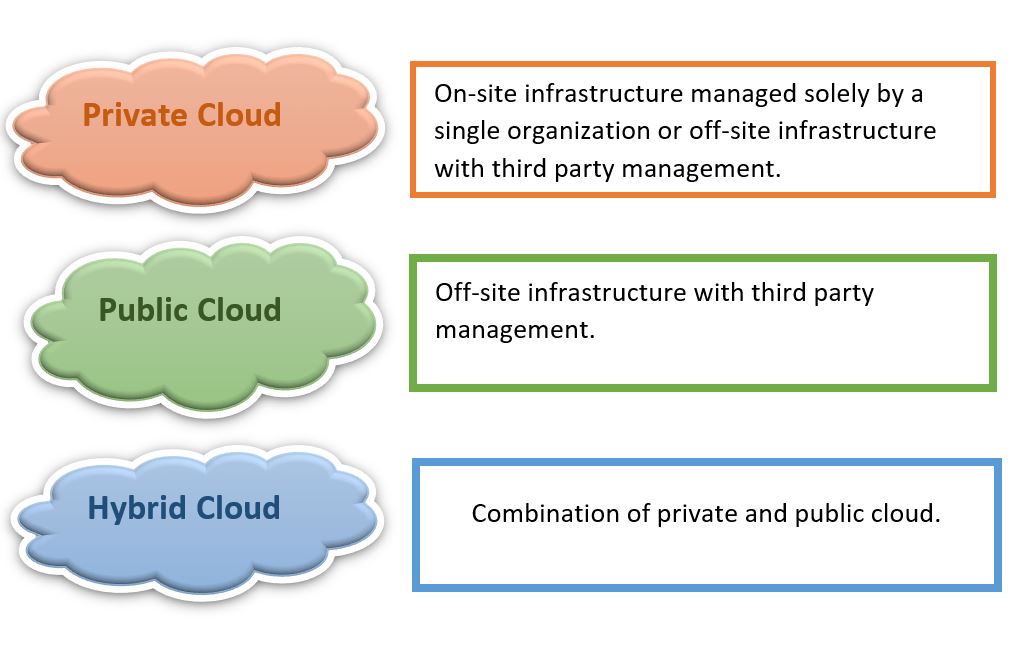
| + | When deploying new solutions Departments should select cloud models in the following order of priority. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:Cloud model.jpg|800px |frameless|center]] | ||
| + | === Public Cloud === | ||
| + | Computing cloud resources are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider (CSP). | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | === Hybrid Cloud === | ||
| + | Public and private clouds are used with data and applications communicating between the two. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | === Private Cloud=== | ||
| + | Computing cloud resources (that can be located on the premises or hosted by a third-party CSP) are dedicated to one organization and maintained on a private network. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | === Non-Cloud === | ||
| + | A traditional IT environment for hosting legacy applications that cannot be deployed to a cloud environment | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | == Cloud Benefits == | ||
| + | * Cost effectiveness: IT infrastructure is costly and labor intensive. Cloud offers an opportunity to offset these costs. | ||
| + | * High flexibility and scalability | ||
| + | * Multiuser | ||
| + | * High accessibility from any device anytime | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Cloud Computing Service Models == | ||
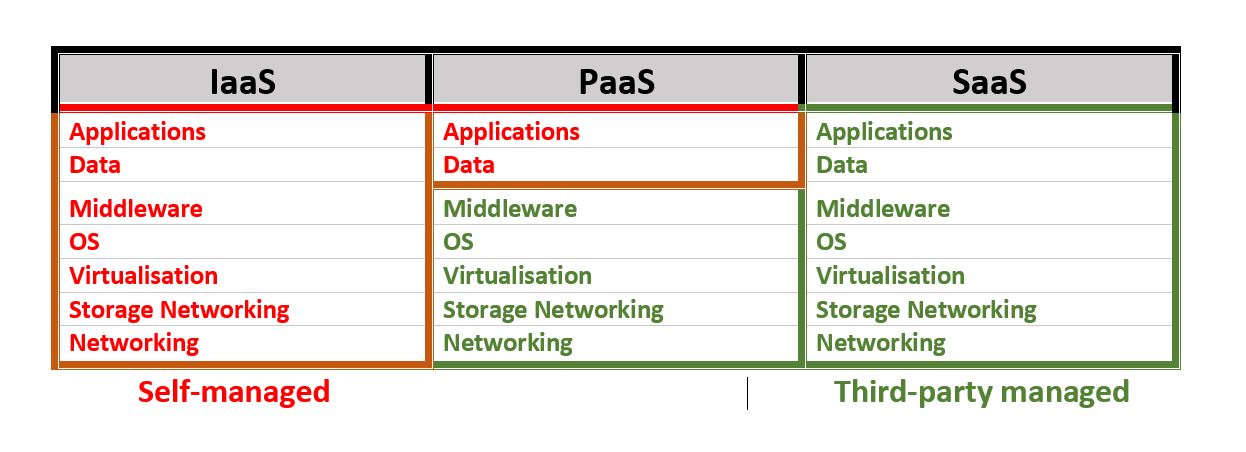
| + | The National Institute of Standards and Technology defines 3 cloud service models: | ||
| + | [[File:Iaas.jpg|800px|frameless|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service === | ||
| + | IaaS offers services such as pay-as-you-go storage, networking, and virtualization. | ||
| + | IaaS gives users cloud-based alternatives to on-premise infrastructure, so businesses can avoid investing in expensive on-site resources. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | === PaaS – Platform as a Service === | ||
| + | In PaaS, the vendor provides hardware and software tools over the internet, and people use these tools to develop applications. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | === SaaS – Software as a Service === | ||
| + | Platforms make software available to users over the internet, usually for a monthly subscription fee. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | == GC Cloud adoption principles == | ||
| + | The key principles developed are to ensure that the GC maximizes its benefit and at the same time complies with key data security requirements. The principles can be found in the Government of Canada Cloud Adoption Strategy. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | == Cloud Implementation Approach == | ||
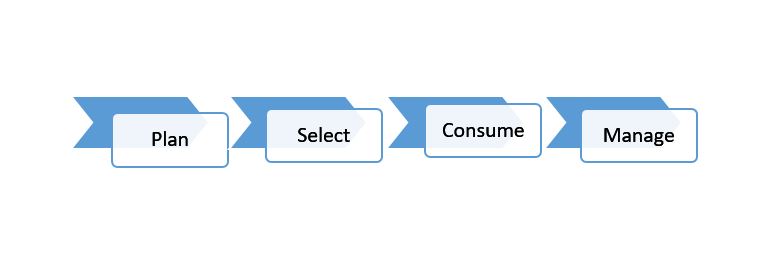
| + | TBS in collaboration with other departments had developed a 4 phases approach to implementing cloud. The diagram below depicts the developed approaches. | ||
| + | [[File:Bussiness context.jpg|800px|frameless|center]] | ||
| + | == Considering Business Context == | ||
| + | There's four factors to be considered when planning for cloud migration: Business, Information, Application, and technology while. For more information read the Government of Canada Right Cloud Selection Guidance. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | If you would like to learn more about the Cloud adoption Strategy of the Government of Canada click [https://www.canada.ca/en/government/system/digital-government/modern-emerging-technologies/cloud-services/government-canada-cloud-adoption-strategy.html here] or visit our [[Policy|Policy section]].</big> | ||
| + | </big><br> | ||
{{GC Cloud Information Centre Footer}} | {{GC Cloud Information Centre Footer}} | ||
| + | __FORCETOC__ | ||
Latest revision as of 13:34, 26 February 2020
Guidance
Overview
The GC Cloud first strategy indicates that when evaluating new IT investments, initiatives, strategies and projects, Departments should consider Cloud options first.
Learn more about the Cloud first strategy by clicking here.
What is the Cloud?
Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing resources (from applications to data centres) over the Internet on a pay-for-use basis
Cloud deployment models
When deploying new solutions Departments should select cloud models in the following order of priority.
Public Cloud
Computing cloud resources are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider (CSP).
Hybrid Cloud
Public and private clouds are used with data and applications communicating between the two.
Private Cloud
Computing cloud resources (that can be located on the premises or hosted by a third-party CSP) are dedicated to one organization and maintained on a private network.
Non-Cloud
A traditional IT environment for hosting legacy applications that cannot be deployed to a cloud environment
Cloud Benefits
- Cost effectiveness: IT infrastructure is costly and labor intensive. Cloud offers an opportunity to offset these costs.
- High flexibility and scalability
- Multiuser
- High accessibility from any device anytime
Cloud Computing Service Models
The National Institute of Standards and Technology defines 3 cloud service models:
IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS offers services such as pay-as-you-go storage, networking, and virtualization.
IaaS gives users cloud-based alternatives to on-premise infrastructure, so businesses can avoid investing in expensive on-site resources.
PaaS – Platform as a Service
In PaaS, the vendor provides hardware and software tools over the internet, and people use these tools to develop applications.
SaaS – Software as a Service
Platforms make software available to users over the internet, usually for a monthly subscription fee.
GC Cloud adoption principles
The key principles developed are to ensure that the GC maximizes its benefit and at the same time complies with key data security requirements. The principles can be found in the Government of Canada Cloud Adoption Strategy.
Cloud Implementation Approach
TBS in collaboration with other departments had developed a 4 phases approach to implementing cloud. The diagram below depicts the developed approaches.
Considering Business Context
There's four factors to be considered when planning for cloud migration: Business, Information, Application, and technology while. For more information read the Government of Canada Right Cloud Selection Guidance.
If you would like to learn more about the Cloud adoption Strategy of the Government of Canada click here or visit our Policy section.