Important: The GCConnex decommission will not affect GCCollab or GCWiki. Thank you and happy collaborating!
Difference between revisions of "Earth Observation Data Management System (EODMS)"
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
ENVIRONMENT CANADA - CANADIAN ICE SERVICE | ENVIRONMENT CANADA - CANADIAN ICE SERVICE | ||
| − | [1] The Climate Processes Section within the Climate Research Division currently uses Sentinel-1 EW GRDM for researching Arctic sea ice dynamics and melt processes. As part of | + | [1] The Climate Processes Section within the Climate Research Division currently uses Sentinel-1 EW GRDM for researching Arctic sea ice dynamics and melt processes. As part of the analyses, a variety of sea ice motion datasets are generated (e.g. automated daily Pan-Arctic motion, sub-daily regional AOIs) for collaborators working in Government Operations/Research as well as Academic Research. |
[2] Having access to the high-speed connection is critical for the timeliness of the analysis and ice motion products generated in addition to maintaining the capacity to keep pace with the rate of SAR data acquisition. With the previous connection the delay between image download, analysis and product generation was a large bottleneck whereas with DHUS National Mirror access we can automate same-day or 1-day-previous sea ice motion products at Pan-Arctic scale. Pan-Arctic processing was basically impossible using the Copernicus Open-Access hub due to the transfer rate bottleneck and cloud-rehosted S1 data collections at the time were not a solution as access to the L1 GRD products was required. | [2] Having access to the high-speed connection is critical for the timeliness of the analysis and ice motion products generated in addition to maintaining the capacity to keep pace with the rate of SAR data acquisition. With the previous connection the delay between image download, analysis and product generation was a large bottleneck whereas with DHUS National Mirror access we can automate same-day or 1-day-previous sea ice motion products at Pan-Arctic scale. Pan-Arctic processing was basically impossible using the Copernicus Open-Access hub due to the transfer rate bottleneck and cloud-rehosted S1 data collections at the time were not a solution as access to the L1 GRD products was required. | ||
Revision as of 03:01, 15 October 2019
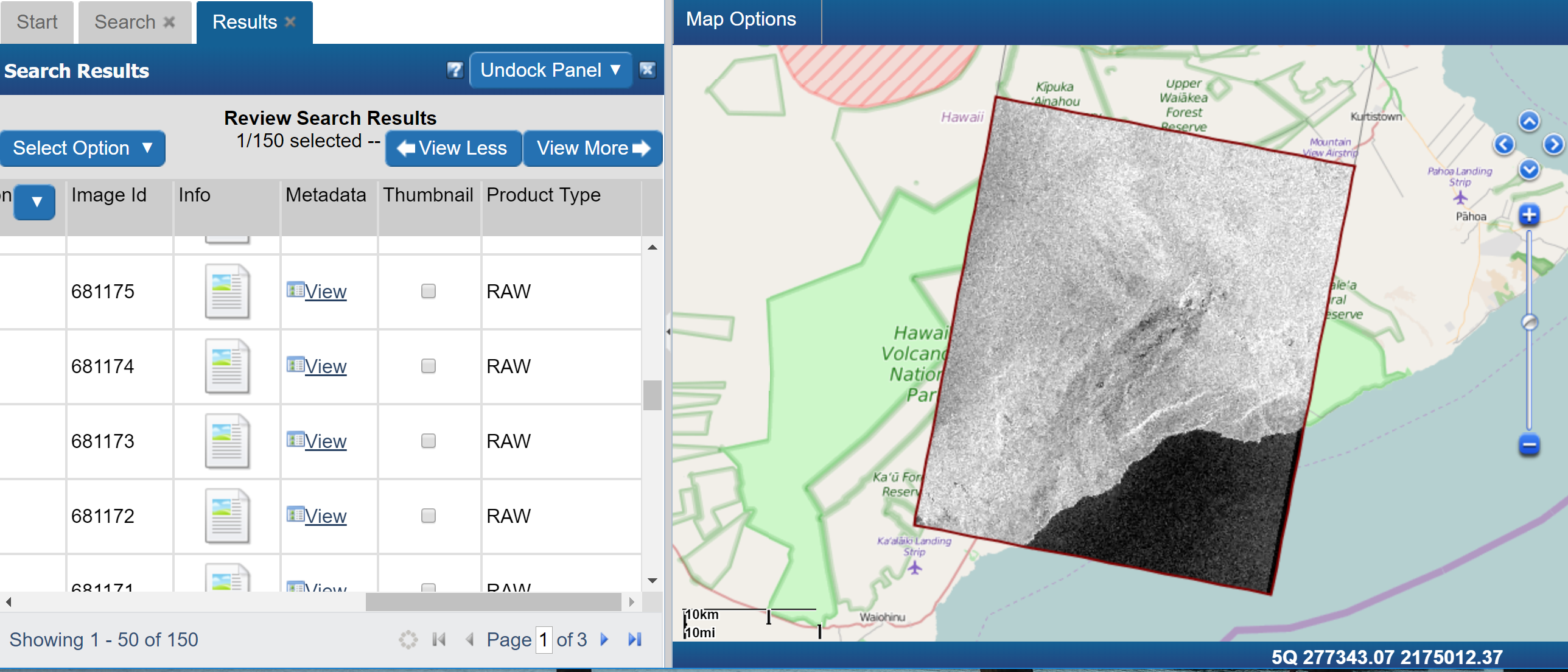
What is EODMS?[edit | edit source]
The Earth Observation Data Management System (EODMS) is a fully integrated geospatial platform provided by NRCan/RNCan to the general public to discover and access authoritative Earth Observation (EO) data. _
The site is located at https://www.eodms-sgdot.nrcan-rncan.gc.ca/index_en.jsp
History[edit | edit source]
With the second largest landmass on earth and the longest coastline in the world, Canada relies on satellite technology to monitor its land and borders. Providing access to this technology is a core mandate of NRCan's Canada Centre for Mapping and Earth Observation (CCMEO). Through partnerships with government stakeholders, strong links to academia and the private sector, including international collaborations, CCMEO ensures that satellite data is available to serve the needs of the Canadian Government and all Canadians. Since 1971, CCMEO has accumulated an archive in excess of 1 PB of Earth Observation (EO) data. This data originated from various satellites and airborne sensors. The 2012 Canadian Federal Budget included NRCan’s revitalization plan which sought to maintain and improve Canada’s EO satellite capacity and access to this data. This plan was realised through the purchase and installation of four (4) new antennas as well as the brand new Earth Observation Data Management System which replaced several legacy systems.
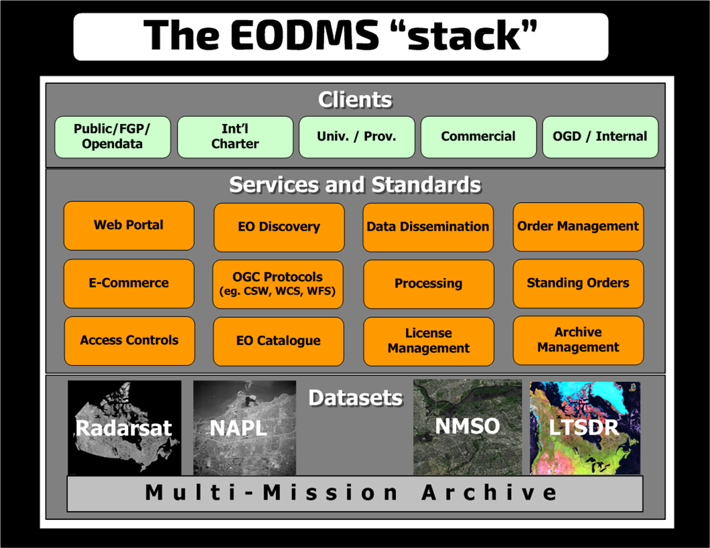
Services[edit | edit source]
Today, CCMEO delivers several EO data services in support of the Government of Canada’s priorities on the economic development of natural resources, the North, safety, security, sovereignty, and environmental monitoring.
EODMS[edit | edit source]
Data services delivered by EODMS include:
- The user-access-controlled (i.e. Government of Canada only) discovery and ordering of RADARSAT 2 (R2) and RADARSAT Constellation Mission (RCM) product as well as commercial satellite imagery (CSI) procured through the NMSO (i.e. COSMOS-Skymed, Deimos-2, DMC, EROS-B, Flock1-ISS, Flock1-SSO, GeoEye-1, GF-1, GHGSat-D, IKONOS, IRS1C-LISS3, IRS1C-PAN, IRS1C-WiFS, IRS1D-LISS3, IRS1D-PAN, IRS1D-WiFS, IRSP6-AWiFS, IRSP6-LISS3, IRSP6-LISS4, KOMPSAT-2, KOMPSAT-3, KOMPSAT-5, PLEIADES, QuickBird-2, RapidEye, SPOT-4, SPOT-5, SPOT-6, SPOT-7, TanDEM-X, Terra, Terra/Aqua, TerraSAR-X, WorldView-1, WorldView-2, WorldView-3, WorldView-4, ZY-3).
- The generic public discovery of RAW RADARSAT-1, RADARSAT-2 , and RCM Science Data.
- The general public discovery and download of RADARSAT-1 Open Data Products
- The general public discovery and download of Canada Centre for Remote Sensing (CCRS) Thematic Data Sets,
- The general public discovery and ordering of the National Air Photo Library
- EODMS is also fully OGC compliant having implemented several standards such as Web Map Tile Service (WMTS), Web Coverage Service (WCS), Catalog Services for the Web (CSW) to name a few. EODMS also implements several geospatial ISO standards including ISO 19115 and ISO 19139.
Multi-Mission Archive (MMA)[edit | edit source]
The storage backbone of EODMS is CCMEO’s Multi-Mission Archive (MMA) which is the Canadian authorised repository of over 1PB of RADARSAT-1, RADARSAT-2, RCM, NAPL and NMSO commercial imagery. The capacity of the archive is currently 4 PB and growing. The data is stored robustly using redundant storage and securely to comply with RSSSA laws on access controls and dissemination.
SENTINEL CANADIAN MIRROR SITE[edit | edit source]
USER STORIES[edit | edit source]
ENVIRONMENT CANADA - CANADIAN ICE SERVICE [1] The Climate Processes Section within the Climate Research Division currently uses Sentinel-1 EW GRDM for researching Arctic sea ice dynamics and melt processes. As part of the analyses, a variety of sea ice motion datasets are generated (e.g. automated daily Pan-Arctic motion, sub-daily regional AOIs) for collaborators working in Government Operations/Research as well as Academic Research. [2] Having access to the high-speed connection is critical for the timeliness of the analysis and ice motion products generated in addition to maintaining the capacity to keep pace with the rate of SAR data acquisition. With the previous connection the delay between image download, analysis and product generation was a large bottleneck whereas with DHUS National Mirror access we can automate same-day or 1-day-previous sea ice motion products at Pan-Arctic scale. Pan-Arctic processing was basically impossible using the Copernicus Open-Access hub due to the transfer rate bottleneck and cloud-rehosted S1 data collections at the time were not a solution as access to the L1 GRD products was required. DEFENSE RESEARCH [1] On behalf of operational partners within DND, DRDC Ottawa uses Sentinel-1 data acquired over the SOIN (Spaceborne Ocean Intelligence Network) area-of-interest off the coast of Halifax, in developing tools for: 1) ocean feature detection and analysis; and 2) ship detection and surveillance. In both cases, the Sentinel-1 images and the Sentinel-1 level-2 radial velocity (RVL) products are used and evaluated in synergy with RADARSAT-2 (and soon RCM) imagery. [2] DHUS National Mirror services are required for three reasons: 1) due to network architecture, the division has difficulty in accessing both the Copernicus Open hub and the API hub; 2) the division downloads hundreds of S1 image frames per month requiring high-speed internet access; and, 3) the division does not have staff resources to manage and create our own automatic downloading service from the Copernicus data hub.
Government and Special Access (NMSO, RADARSAT)[edit | edit source]
NMSO-CSI[edit | edit source]
The NMSO-CSI is the Government of Canada's initiative to cut down on the procurement of duplicate commercial satellite imagery across the public service. All departments with commercial satellite imagery needs should aim to route all procurement through NMSO E60SQ-120001 after which imagery will be loaded on to EODMS to be re-used (i.e. discovered and downloaded) by the whole of government.
All Government of Canada (GC) employees can have free access to NMSO Commercial Satellite Imagery (CSI) already purchased by the GC. Simply create an account EODMS and then send a request to your Department NMSO point of contact (PoC) for your added privileges. You can find more information on our EODMS_NMSO page as well as the request form and your PoC on our GCPedia (Government-only) page, EODMS Account Approvals for Government and Special Access
RADARSAT[edit | edit source]
Did you know that all Government of Canada (GC) employees have access to RADARSAT-2 and RCM products for free? Simply create an EODMS account and contact the Canadian Space Agency Order Desk for more information (ASC.r-sat.CSA@Canada.ca). (Learn more about RADARSAT)
CSA Special Access Programs[edit | edit source]
Did you know that CSA coordinates several [RADARSAT special access programs] to encourage the use of space data including the The International Charter: Space and Major Disasters. Find out more here.
EODMS accounts are granted to, and must only be used by the specified user; accounts are assigned to individuals (authorized users), and not to Departments or groups of people. Both accounts and passwords remain the property of the Government of Canada, and cannot be transferred to other individuals. All accounts are subject to the policies and regulations of the Government of Canada (e.g., the Treasury Board Policy on the Use of Electronic Networks and the NRCan Policy on the Use of Electronic Networks)
What's New?[edit | edit source]
The upgrade to EODMS (from NEODF) brings new support for previously undiscover-able NMSO commercial imagery including DMC Constellation, TerraSAR-X, SPOT-4 to 7, Cosmo Skymed. There is also new support for the RADARSAT-2 NITF format. Prior to this users would have to look for this data without the help of a map on the NEODF FTP directory structure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)[edit | edit source]
Please visit our FAQ page for training information.