Important: The GCConnex decommission will not affect GCCollab or GCWiki. Thank you and happy collaborating!
Handbook for Regulatory Proposals: Performance Measurement and Evaluation Plan
We have archived this page and will not be updating it.
You can use it for research or reference. Consult our Cabinet Directive on Regulations: Policies, guidance and tools web page for the policy instruments and guidance in effect.
Introduction
This handbook outlines the purpose of a Performance Measurement and Evaluation Plan (PMEP) for regulatory activities and provides guidance for its development and for completing the PMEP Template. The handbook supports the implementation of the Cabinet Directive on Streamlining Regulation (CDSR).
The intended users of this handbook are government officials who need to develop and implement a PMEP for their regulatory proposals as well as the analysts in the Regulatory Affairs Sector of the Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat (Secretariat) who perform a challenge function.
Throughout the handbook, regulatory activities are understood to mean the regulation(s), the regulatory program, and the regulatory program's related activities, such as communications, inspection, and enforcement.
What are the performance measurement requirements under the Cabinet Directive on Streamlining Regulation?
The requirements for carrying out performance measurement for regulatory activities are outlined in Section 4.6 of the CDSR, "Measuring, evaluating, and reviewing regulation." They are also outlined in the Regulatory Impact Analysis Statement (RIAS) Template.
What is the purpose of a Performance Measurement and Evaluation Plan?
The purpose of a PMEP is to ensure that regulatory activities continue to meet their initial policy objectives and are accordingly renewed on an ongoing basis. A PMEP provides a concise statement or road map to plan, monitor, evaluate, and report on results throughout the regulatory life cycle. When implemented, it helps a regulator:
- ensure a clear and logical design that ties resources and activities to expected results;
- describe the roles and responsibilities of the main players involved in the regulatory proposal;
- make sound judgments on how to improve performance on an ongoing basis;
- demonstrate accountability and benefits to Canadians;
- ensure reliable and timely information is available to decision makers in the regulatory organizations and central agencies as well as to Canadians; and
- ensure that the information gathered will effectively support an evaluation.
When is a Performance Measurement and Evaluation Plan required?
Before submitting a regulatory proposal, departments and agencies are expected to conduct an assessment, which is based on the and performed in collaboration with the Secretariat's Regulatory Affairs Sector, to determine the level of impact (Low, Medium, or High) of the proposed regulation.
Completion of a PMEP Template is required when the answer to one or more of questions 1 through 6 in the Triage Statement is "High." For regulatory proposals of Medium impact, completing a PMEP Template is optional and left to the discretion of the regulatory organization.
Where are the regulatory activities situated in the department's Program Activity Architecture and Performance Measurement Framework?
When developing the PMEP, it is important to ask the following question: How does this PMEP fit into the departmental Management, Resources, and Results Structures (MRRS), specifically the Program Activity Architecture (PAA) and the Performance Measurement Framework (PMF)?
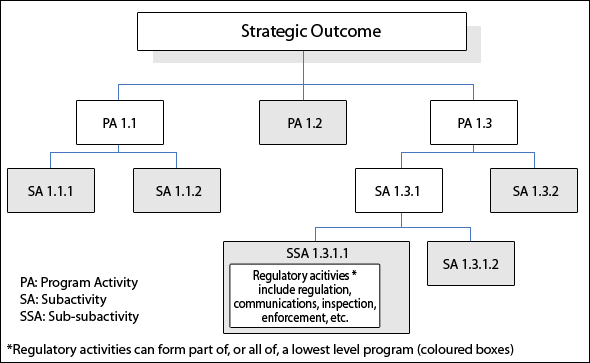
Regulatory activities would be represented, when appropriate, in a departmental PAA and supporting PMF as a program's[1] lowest level component, i.e., a program's sub-subactivity level (see graphic under Linkage to the Program Activity Architecture). Where regulatory activities are significant to understanding why and how funds are being spent to achieve a program's stated expected results, they must be mentioned in the program description unless a compelling rationale for omitting them is provided. Program managers will need to consider how performance indicators supporting regulatory activities factor into a program's PMF. For example, regulatory activity indicators may support a program output tracked in the PMF or a program's expected result. Managers are strongly encouraged to consult with key corporate groups (e.g., heads of Evaluation, program performance measurement teams or units) to determine the most appropriate way to align performance indicators within the MRRS.
To ensure the departmental PAA and PMF reflect a new PMEP, they should be updated in accordance with the next scheduled review of the PAA and PMF, but only after the regulation has been published in Canada Gazette, Part II.
How to complete a Performance Measurement and Evaluation Plan Template
This section contains a description of the nine core components of the PMEP Template (see Appendix A). Definitions related to performance measurement can be found in the Results-Based Management Lexicon. Information from the PMEP Template is carried forward into the Performance measurement and evaluation section of the RIAS. If the regulatory proposal involves a Treasury Board submission, the PMEP should be consistent with that submission (see A Guide to Preparing Treasury Board Submissions).
Description and Overview of the Regulatory Proposal
The introductory component of a PMEP should provide a thorough description of the problems and risks that the regulatory proposal aims to address, as identified in the Triage Statement. This section should also specify the proposed regulation's target audience, the intended beneficiaries, and the behavioural changes it seeks to bring about among specific groups. This element of the PMEP Template is linked to the Issue, Objectives, and Description sections of the RIAS.
The questions to be answered are as follows:
- What is the issue the regulatory proposal aims to address?
- What evidence exists to show that there is an issue?
- Why is the issue important?
- In concrete terms, what are the objectives of the regulatory proposal?
- How will the regulatory proposal achieve the objectives for solving or mitigating the issue?
- Who are the target audiences (i.e., regulated individuals and organizations) of the proposed regulation?
- Who are the intended beneficiaries of the proposed regulation (e.g., Canadian public, specific groups within the Canadian public such as children under the age of four)?
- What behavioural changes in the target audience need to be addressed (e.g., awareness, understanding, capacity, compliance)?
This section should also describe how the proposed regulation fits into the bigger picture (i.e., how it contributes to the regulatory program, the department's strategic outcomes (PAA), other overarching initiatives). Furthermore, identify if and how the regulatory activities cut across multiple regulatory organizations. Finally, indicate how the information summarized and reported will be used to improve the performance of the regulatory activities.
Logic Model
A logic model, which is composed of a graphic and accompanying text, tells the story of regulatory activities. It connects the inputs (resources) and activities (what one does) to the outputs (products or services generated from the activities), the groups reached (regulated parties or beneficiaries), and the expected outcomes of the initiative (the sequence of changes among groups outside the control of the regulatory organization). In its simplest form, the logic model is composed of the following five logically interrelated components.
- Inputs: The human and financial resources used to undertake the regulatory activities and consequently produce outputs (i.e., services and products). Inputs include personnel, physical facilities, equipment, materials, and funding. In some cases, they include the legislative or regulatory authority necessary to undertake regulatory activities.
- Activities: Actions that the department or agency undertakes to produce its outputs. For instance, inspection and licensing are two regulatory activities that are commonly found in regulatory organizations.
- Outputs: The products or services produced by regulatory activities. Outputs are deliverables wholly under the control of an organization. The results that occur beyond outputs are not within the full control of the regulatory organization.
- Target groups (reach): The individuals, groups, or organizations that the regulatory activity is intended to reach and influence. This includes both regulatees (i.e., those subject to regulations) and other key groups who are important to the success of the initiative (e.g., public, private, and not-for-profit organizations, other institutions, and individual Canadians, among others).
- Outcomes: Results attributable to a regulatory organization. Outcomes are not the direct result of a single regulatory activity; rather, they are affected by what the organization does. Outcomes are further qualified as immediate (also known as direct), intermediate, or ultimate and are linked to the target groups that the regulatory organization is trying to influence.
The problems or risks identified in Section 1 of the PMEP Template help to define the inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes stated in the logic model. See Appendix B for more on how risks and problems set the vital context for results (this is also covered in a course offered at the Canada School of Public Service).
In developing the logic of the regulatory proposal, organizations can draw on other departmental documents related to MRRS. Where possible, the logic model for the regulatory activity should be linked to related programs and the strategic outcomes of the regulatory organization.
Logic models should be reviewed and validated in conjunction with the appropriate department or agency personnel to confirm the accuracy of the program logic and to facilitate buy-in among those who will be involved in implementing and maintaining the ongoing performance measurement monitoring system. In the spirit of ongoing consultation and engagement with stakeholders, departments and agencies are encouraged to involve, when appropriate, external stakeholders with an interest in the regulatory activity.
Indicators
An indicator is a quantitative or qualitative means of gauging an initiative's performance or the progress made toward its expected desired results. Indicators operationally describe the intended output or outcome one is seeking to achieve over time.
Indicators should be developed from the logic model in the PMEP Template. Indicators need to be prioritized and limited in number when selected for monitoring. It is more effective to measure the critical few rather than the trivial many. A small set[2] of highly meaningful indicators need to be specified to track overall performance with respect to the intended outcomes and policy objectives of the regulatory proposal (e.g., health, safety, security, environmental protection, business and trade, Aboriginal prosperity). Where possible, these indicators should be consistent with, and ideally support, indicators found in the department's PMF.
Indicators should be expressed as numerical forms when possible (e.g., as raw numbers, averages, percentages, rates, ratios, or indexes).[3] Where qualitative indicators are used, they should be objectively verifiable. Certain criteria should be kept in mind when selecting indicators. Indicators should be:
- Relevant and valid;
- Prioritized and limited in number;
- Balanced and comprehensive;
- Meaningful and understandable;
- Timely and actionable; and
- Cost-effective to measure.[4]
Hint Developing Indicators—A Short-Hand Approach
When developing performance indicators, it is useful to ask the following: What would you see or hear if the expected results you have described are being achieved? The answer to this question should provide you with strong guidance as to what the indicator of performance should be.
Once you have answered the question, you will want to define the indicator as follows:
- Suggest the measure of change, such as its number, proportion, percentage, rate, ratio, amount, or level.
- Specify who is changing. This may include the population target group, program participant, client, individual, organization, agency, or community. The more you specifically describe the group who should be changing or from whom you expect a reaction, the more precise the indicator.
- Specify what is changing or happening. This may include changes to awareness, attitude, knowledge, skill, aspirations, commitments, behaviours, or practices. It may also include simple reactions such as perception or satisfaction. Note that this may not always be a change per se; sometimes, one is seeking to maintain existing reactions and behaviours.
A key principle for developing indicators is that they should always follow the logic of an initiative's expected results. Examples are as follows:
| Level | Examples |
|---|---|
| Ultimate Outcomes
The highest level outcome that can be reasonably attributed to a policy, program, or initiative and that is the consequence of one or more intermediate outcomes having been achieved. Such outcomes represent a change of state in a target population. |
|
| Intermediate Outcomes
An outcome that is expected to logically occur once one immediate outcome (or more) has been achieved. |
|
| Immediate Outcomes
An outcome that is directly attributable to the outputs of a policy, program, or initiative. |
|
| Outputs
Direct products or services stemming from the activities of an organization, policy, program, or initiative and usually within the control of the organization itself. |
|
Measurement and Reporting
After selecting a set of indicators, the next step is to establish an approach for ongoing performance measurement and reporting. It is common to summarize a measurement and reporting strategy using a tabular format. The table would include a description of the element being measured (output or outcome), the indicator itself, a description of the data source for the indicator and the methods used to collect the data, a description of how a baseline measurement will be established (existing information or new baseline based on first measurement), performance targets for the indicator, a description of how often the indicator will be measured, and a description of who is responsible for measurement and data collection. Much of this data should be available in the regulatory proposal's cost-benefit analysis and RIAS. The table could also address all levels of the PMEP's logic model (e.g., output and immediate, intermediate, and ultimate outcomes).
To facilitate the update of the PMF, the following table should be used in the PMEP Template; however, it could be expanded to define other elements beyond what is required to update the PMF.
| Strategic Outcome / Expected Result / Output | Performance Indicator | Data Source | Frequency of Data Collection | Target | Date to Achieve Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The choice of a data source and collection method will depend on the type of performance indicators and the purpose of the information being gathered. The choice of a data source will also depend on whether the information is being collected on a regular basis (for ongoing monitoring purposes) or periodically (as part of an evaluation). Data can be collected from various sources, as follows:
- Administrative data—Information that is being collected through day-to-day activities, such as permit and licensing applications, audits, inspections, and enforcement. Regulatory organizations should be mindful of the administrative burden that data collection may place on businesses and individuals.
- Primary data—Information that is collected through specialized data collection exercises, such as surveys, focus groups, expert panels, or specialized evaluation studies.
- Secondary data—Data that have been collected by other organizations, such as national statistics on health and economic status.
Baseline measurements establish critical reference points from which subsequent changes in indicators can be measured. If reliable historical data on the performance indicator exists, they should be used. Otherwise, it will be necessary to collect baseline data at the first opportunity.
Performance targets consist of projected indicator values for quarterly, semi-annual, or annual performance periods. The target for the regulatory proposal should relate to the analysis (e.g., cost-benefit analysis and risk assessment) that supported the decision to regulate in the first place. Targets can also be set for achieving certain levels of performance in the longer term. Target measurements can be used as interim information about how particular indicators are working. Such information can also be useful for annual reporting and budgeting exercises. Suggested guidelines for setting targets include the following:
- Setting targets based on previous performance (i.e., the level at which performance is no longer deemed "a problem");
- Setting targets using the performance level achieved by the most successful performance to date;
- Setting targets using the performance level achieved by averages of past performance;
- Setting targets using performance levels achieved by other jurisdictions or by private firms with similar activities;
- Making sure that the targets chosen are feasible given the program's budget, staffing, and anticipated influence; and
- Identifying developments—internal and external—that may affect the program's ability to achieve desired outcomes.
Regulatory organizations have a responsibility to report to Canadians on an annual basis through the Report on Plans and Priorities (RPP) and Departmental Performance Report (DPR). This reporting responsibility provides an excellent opportunity to roll up the findings of ongoing performance measurement activities. Other reporting instruments such as websites, annual reports, and newsletters are also effective and timely means for communicating progress on a regulatory proposal to Canadians.
Evaluation Strategy
Regulatory organizations are required to evaluate their regulatory activities in accordance with the time frames and cycle established in the Policy on Evaluation, which defines evaluation as "the systematic collection and analysis of evidence on the outcomes of programs to make judgments about their relevance, performance and alternative ways to deliver them or to achieve the same results." The evaluation of regulatory activities should be referenced in the annual departmental evaluation plan.
The Evaluation Strategy is a high-level framework that identifies and documents key evaluation questions and the type of data required to address the evaluation questions. The purpose of the Evaluation Strategy is as follows:
- Allows program managers and the Head of Evaluation to ensure that the performance measurement strategy generates sufficient performance data to support the evaluation;
- Allows program managers and the Head of Evaluation to ensure that needed administrative data, in addition to what will be collected through the performance measurement strategy, are available at the time of the evaluation;
- Allows the Head of Evaluation to identify what additional data will need to be collected to support the evaluation; and
- Allows program managers to give the Head of Evaluation advance notice on evaluation commitments that can inform the departmental evaluation plan.
The Evaluation Strategy should include the time frame and responsibilities for developing the evaluation framework and for completing the evaluation. Provided the evaluation addresses the core issues outlined in Annex A of the Directive on the Evaluation Function, regulatory organizations have the flexibility to determine the evaluation's approach and level of effort in accordance with the impact of the regulatory activities as identified in the Triage Statement.
It is expected that the Evaluation Strategy will comply with the requirements of the Treasury Board Policy on Evaluation and Directive on the Evaluation Function. A valuable resource when developing the Evaluation Strategy is the Guide for the Development of Performance Measurement Strategies and for Ensuring that They Effectively Support Evaluation (forthcoming). Regulatory organizations are also encouraged to consult their Head of Evaluation when developing the Evaluation Strategy.
Linkage to the Program Activity Architecture
Briefly describe where the regulatory activities are situated in the PAA. If the regulatory activities do not yet figure in the PAA, indicate when they are expected to be integrated. An example of how regulatory activities are represented in a PAA follows.
Regulatory Affairs Sector Review
Before the PMEP is signed off by the regulatory organization's responsible Assistant Deputy Minister, a draft copy of the PMEP must be sent to the Secretariat's Regulatory Affairs Sector portfolio analyst for review to confirm that the PMEP meets CDSR requirements. When seeking confirmation from the Secretariat's Regulatory Affairs Sector, the Head of Evaluation should have provided comments on the PMEP.
Assistant Deputy Minister Sign-off
The Head of Evaluation must review the PMEP and agree that it effectively supports the conduct of an eventual evaluation. The PMEP is then signed by the Assistant Deputy Minister (or equivalent) responsible for the regulatory proposal.
Approval criteria for the Assistant Deputy Minister (or equivalent) are the following:
- The scope and detail of the PMEP are commensurate with the impact of the regulatory proposal;
- The PMEP's content is accurate and reflects the design, implementation, and evaluation of the regulatory activities;
- There is commitment to monitor, evaluate, and report on the performance of the regulatory proposal, including implementation of the PMEP, through the use of progress information to support decision making and the conduct of periodic evaluation exercises according to the departmental evaluation plan;
- Accountabilities for delivery, collection, and timely reporting of performance information and for evaluation activities are clear;
- Resources are sufficient to implement the PMEP; and
- The Head of Evaluation has reviewed the PMEP and agrees that it effectively supports the conduct of an eventual evaluation.
All sign-offs on the PMEP must be obtained before final approval of the RIAS by the Secretariat's Regulatory Affairs Sector. The regulatory organization must send two signed copies of the final PMEP to Regulatory Affairs.
Departmental Contact
Identify the contact person(s) and contact information for enquiries.
What needs to be in the Regulatory Impact Assessment Statement?
A summary (maximum 2 pages) of the PMEP is to be included in the Performance measurement and evaluation section of the RIAS, consisting of the following key elements:
- A summary of how the regulatory activities connect the inputs and activities to the outputs, target groups, and expected outcomes of the initiative (i.e., summary of the logic model);
- A description of the indicators through which changes in outputs and outcomes of the regulatory proposal will be measured;
- A description of how and when the information will be summarized, reported, and used to improve the performance of the regulatory activities;
- An outline of how (i.e., methodology) and when the regulatory activities will be evaluated; and
- Indication of the PMEP's availability upon request.
Who can provide advice and assistance and where can you get training?
Departmental performance measurement and evaluation specialists can provide guidance on the articulation of key outcomes, results logic, and intended policies, the identification and selection of indicators, and the development of strategies for ongoing monitoring and reporting as well as for evaluation. Specialists involved in the cost-benefit analysis of the regulatory proposal may also be of value to you. Information management and information technology (IM/IT) personnel can also contribute to the PMEP development process by providing expertise on data system design or redesign. They can identify what is already being collected, what would be easy to collect, what mechanisms are already in place to collect data, and what the system implications might be of choosing a certain indicator for regular monitoring.
Notes
- ↑ A program is defined as a group of related resource inputs and activities that are managed as a budget unit to address one or more specific needs and to achieve certain expected results.
- ↑ Regulatory organizations will have to use their judgment to determine how many indicators are needed.
- ↑ The expression of indicators in numerical form does not preclude the use of qualitative information, as shown in the examples found later in this section.
- ↑ Note that in practice, it is not possible to maximize all criteria simultaneously; it is often necessary to trade off performance on some criteria against improvements on other criteria.