Important: The GCConnex decommission will not affect GCCollab or GCWiki. Thank you and happy collaborating!
Difference between revisions of "Metadata"
(Created page with "'''Metadata''' means "data about the data". It's a Structured information that describes a resource and makes it easier to retrieve, use, or manage an information resource<br>...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Metadata''' means "data about the data". It's a Structured information that describes a resource and makes it easier to retrieve, use, or manage an information resource<br> | + | == '''Metadata Definition''' == |
| + | Metadata means "data about the data". It's a Structured information that describes a resource and makes it easier to retrieve, use, or manage an information resource<br> | ||
The "meta" prefix (comes from the Greek preposition and prefix μετά-) means "after" or "beyond", it is used to mean "about". <br> | The "meta" prefix (comes from the Greek preposition and prefix μετά-) means "after" or "beyond", it is used to mean "about". <br> | ||
Metadata can be defined as the data providing information about one or more aspects of the data. <br> | Metadata can be defined as the data providing information about one or more aspects of the data. <br> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
| [[File:HighwayNoMetadata.png|545x545px]] || [[File:HighwayWithMetadata.png|545x545px]] | | [[File:HighwayNoMetadata.png|545x545px]] || [[File:HighwayWithMetadata.png|545x545px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == Why do we need Metadata == | + | === Why do we need Metadata === |
Metadata helps answering the following questions: | Metadata helps answering the following questions: | ||
Who created the data? | Who created the data? | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
However, if not maintained Metadata becomes ineffective over time due to inconsistencies in structure, vocabulary, and spelling. In this light, metadata by itself could be meaningless. | However, if not maintained Metadata becomes ineffective over time due to inconsistencies in structure, vocabulary, and spelling. In this light, metadata by itself could be meaningless. | ||
| − | == Metadata Formats == | + | === Metadata Formats === |
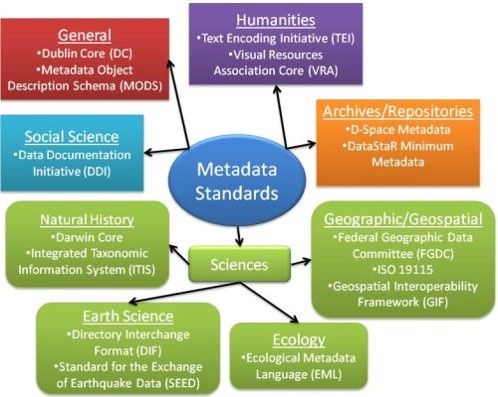
A Structured documentation in XML format can be used to store/exchange metadata based on agreed upon Standards: ISO, DDI, FGDC, EML, Dublin Core, Darwin Core , SAML... | A Structured documentation in XML format can be used to store/exchange metadata based on agreed upon Standards: ISO, DDI, FGDC, EML, Dublin Core, Darwin Core , SAML... | ||
[[File:MetaDataStandards.jpg|345x345px]] | [[File:MetaDataStandards.jpg|345x345px]] | ||
| − | == Metadata tools == | + | === Metadata tools === |
| + | Multiple free and paid tools are available : | ||
| + | * ISA Creator | ||
| + | * Morpho | ||
| + | * OMERO | ||
| + | * Archon | ||
| + | * RightField | ||
| + | * CatMDEdit | ||
| + | * ArcCatalog | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://library.stanford.edu/research/data-management-services/data-best-practices/creating-metadata/metadata-tools More here: Free Metadata tools] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:54, 25 September 2018
Metadata Definition
Metadata means "data about the data". It's a Structured information that describes a resource and makes it easier to retrieve, use, or manage an information resource
The "meta" prefix (comes from the Greek preposition and prefix μετά-) means "after" or "beyond", it is used to mean "about".
Metadata can be defined as the data providing information about one or more aspects of the data.
Metadata is used to summarize basic information about data which can make tracking and working with specific data easier.
The following pictures illustrate the importance of metadata
| Could you recognize this? | Same Junction with its Metadata |
|---|---|
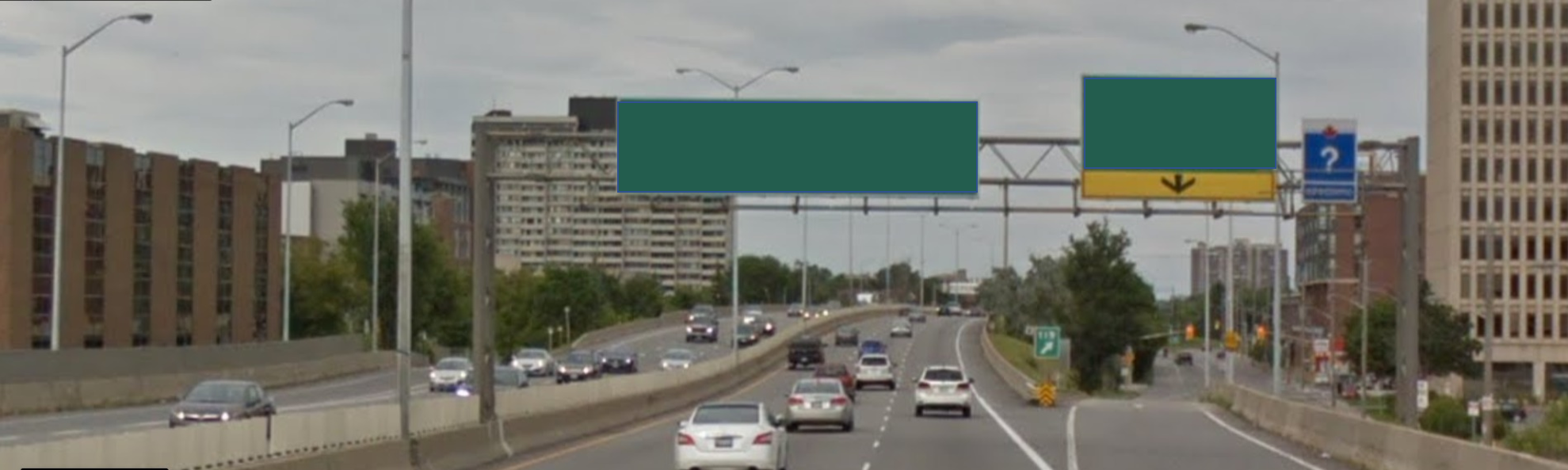 |

|
Why do we need Metadata
Metadata helps answering the following questions: Who created the data? Who maintains it? When were the data collected? When were they published? Where was it collected (geographic location)? What is the content of the data? The structure? Why were the data created? How were they produced/analyzed?
Metadata can be used for:
- Finding/Discovery Data: Metadata makes it much easier to find relevant data. Most searches are done using text (like a Google search), so formats like audio, images, and video are limited unless text metadata is available. Metadata also makes text documents easier to find because it explains exactly what the document is about.
- Using Data: To use a dataset, researchers need to understand how the data is structured, definitions of terms used, how it was collected, and how it should be read.
- Re-using Data: Researchers often want to re-use data collected for another project for their own project. The data still needs to be found and used, but often at a higher level of trust and understanding. Re-using data often requires careful preservation and documentation of the metadata.
However, if not maintained Metadata becomes ineffective over time due to inconsistencies in structure, vocabulary, and spelling. In this light, metadata by itself could be meaningless.
Metadata Formats
A Structured documentation in XML format can be used to store/exchange metadata based on agreed upon Standards: ISO, DDI, FGDC, EML, Dublin Core, Darwin Core , SAML...
Metadata tools
Multiple free and paid tools are available :
- ISA Creator
- Morpho
- OMERO
- Archon
- RightField
- CatMDEdit
- ArcCatalog