Difference between revisions of "ISED Departmental Data Strategy Placemat"
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ('''Francais''': ) ('''Home Page''': ISED Data Strategy) | + | ('''Francais''': [[Stratégie ministérielle d'ISDE en matière de données]]) ('''Home Page''': [[ISED Data Strategy]]) |
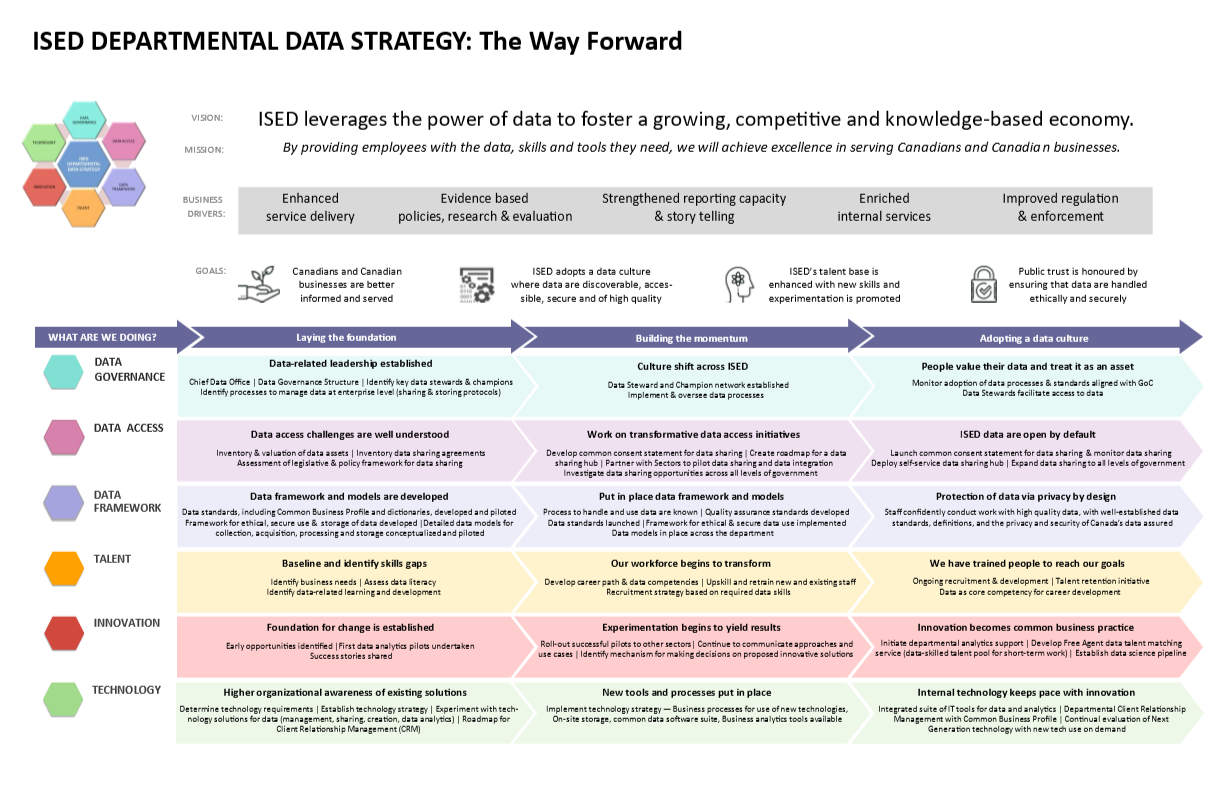
| + | [[File:ThewayforwardplacematENG.png|none|frame]] | ||
== ISED Departmental Data Strategy: The Way Forward == | == ISED Departmental Data Strategy: The Way Forward == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
=== Mission: === | === Mission: === | ||
By providing employees with the data, skills and tools they need, we will achieve excellence in serving Canadians and Canadian businesses. | By providing employees with the data, skills and tools they need, we will achieve excellence in serving Canadians and Canadian businesses. | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | ==== Business Drivers ==== | ||
| + | * Enhanced service delivery | ||
| + | * Evidence based policies, research and evaluation | ||
| + | * Strengthened reporting capacity and story telling | ||
| + | * Enriched internal services | ||
| − | + | * Improved regulation and enforcement | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | + | ==== '''Goals''' ==== | |
| − | Goals | + | * Canadians and Canadian businesses are better informed and served |
| − | + | * ISED adopts a data culture where data are discoverable, accessible, secure and of high quality | |
| − | + | * ISED's talent base is enhanced with new skills and experimentation is promoted | |
| − | + | * Public trust is honoured by ensuring that data are handled ethically and securely | |
| − | + | | | |
| − | What are we doing? | + | | |
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== What are we doing? ==== | ||
There are six pillars of the ISED Data Strategy, each of which has high level initiatives in three phases of implementation; laying the foundation, building the momentum and adopting a data culture. The following table addresses each pillar by phase of implementation. | There are six pillars of the ISED Data Strategy, each of which has high level initiatives in three phases of implementation; laying the foundation, building the momentum and adopting a data culture. The following table addresses each pillar by phase of implementation. | ||
| − | + | == Data Governance == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | === Laying the foundations: '''Data-related leadership established''' === | |
| − | + | * Chief Data Office | |
| − | + | * Data Governance Structure | |
| − | + | * Identify key data stewards & champions | |
| − | + | * Identify processes to manage data at enterprise level (sharing & storing protocols) | |
| − | + | ||
| + | === Building the momentum: Culture shift across ISED === | ||
| + | * Data Steward and Champion network established | ||
| + | * Implement & oversee data processes | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Adopting a data culture: People value their data and treat it as an asset === | ||
| + | * Monitor adoption of data processes & standards aligned with GoC | ||
| + | * Data Stewards facilitate access to data | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Data Access == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Laying the foundations: '''Data access challenges are well understood''' === | ||
| + | * Inventory & evaluation of data assets | ||
| + | * Inventory data sharing agreements | ||
| + | * Assessment of legislative & policy framework for data sharing | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Building the momentum: '''Work on transformative data access initiatives''' === | ||
| + | * Develop common consent statement for data sharing | ||
| + | * Create roadmap for a data sharing hub | ||
| + | * Partner with Sectors to pilot data sharing and data integration Investigate data sharing opportunities across all levels of government | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Adopting a data culture: '''ISED data are open by default''' === | ||
| + | * Launch common consent statement for data sharing & monitor data sharing | ||
| + | * Deploy self-service data sharing hub | ||
| + | * Expand data sharing to all levels of government | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Data Framework == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Laying the foundations: '''Data framework and models are developed''' === | ||
| + | * Data standards, including Common Business Profile and dictionaries, developed and piloted Framework for ethical, secure use & storage of data developed | ||
| + | * Detailed data models for collection, acquisition, processing and storage conceptualized and piloted | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Building the momentum: '''Put in place data framework and models''' === | ||
| + | * Process to handle and use data are known | ||
| + | * Quality assurance standards developed Data standards launched | ||
| + | * Framework for ethical & secure data use implemented | ||
| + | * Data models in place across the department | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Adopting a data culture: '''Protection of data via privacy by design''' === | ||
| + | * Staff confidently conduct work with high quality data, with well-established data standards, definitions, and the privacy and security of Canada's data assured | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Talent == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Laying the foundations: '''Baseline and identify skills gaps''' === | ||
| + | * Identify business needs | ||
| + | * Assess data literacy | ||
| + | * Identify data-related learning and development | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Building the momentum: '''Our workforce begins to transform''' === | ||
| + | * Develop career path & data competencies | ||
| + | * Upskill and retrain new and existing staff | ||
| + | * Recruitment strategy based on required data skills | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Adopting a data culture: '''We have trained people to reach our goals''' === | ||
| + | * Ongoing recruitment & development | ||
| + | * Talent retention initiative | ||
| + | * Data as core competency for career development | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Innovation == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Laying the foundations: '''Foundation for change is established''' === | ||
| + | * Early opportunities identified | ||
| + | * First data analytics pilots undertaken | ||
| + | * Success stories shared | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Building the momentum: '''Experimentation begins to yield results''' === | ||
| + | * Roll-out successful pilots to other sectors | ||
| + | * Continue to communicate approaches and use cases | ||
| + | * Identify mechanism for making decisions on proposed innovative solutions | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Adopting a data culture: '''Innovation becomes common business practice''' === | ||
| + | * Initiate departmental analytics support | ||
| + | * Develop Free Agent data talent matching service (data-skilled talent pool for short-term work) | ||
| + | * Establish data science pipeline | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Technology == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Laying the foundations: '''Higher organizational awareness of existing solutions''' === | ||
| + | * Determine technology requirements | ||
| + | * Establish technology strategy | ||
| + | * Experiment with technology solutions for data (management, sharing, creation, data analytics) | ||
| + | * Roadmap for Client Relationship Management (CRM) | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Building the momentum: '''New tools and processes put in place''' === | ||
| + | * Implement technology strategy | ||
| + | * Business processes for use of new technologies | ||
| + | * On-site storage, common data software suite | ||
| + | * Business analytics tools available | ||
| − | + | === Adopting a data culture: '''Internal technology keeps pace with innovation''' === | |
| − | + | * Integrated suite of IT tools for data and analytics | |
| − | + | * Departmental Client Relationship Management with Common Business Profile | |
| − | + | * Continual evaluation of Next Generation technology with new tech use on demand | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 15:16, 13 January 2021
(Francais: Stratégie ministérielle d'ISDE en matière de données) (Home Page: ISED Data Strategy)
ISED Departmental Data Strategy: The Way Forward
Vision:
ISED leverages the power of data to foster a growing, competitive and knowledge based economy.
Mission:
By providing employees with the data, skills and tools they need, we will achieve excellence in serving Canadians and Canadian businesses.
Business Drivers
|
||
Goals
|
What are we doing?
There are six pillars of the ISED Data Strategy, each of which has high level initiatives in three phases of implementation; laying the foundation, building the momentum and adopting a data culture. The following table addresses each pillar by phase of implementation.
Data Governance
- Chief Data Office
- Data Governance Structure
- Identify key data stewards & champions
- Identify processes to manage data at enterprise level (sharing & storing protocols)
Building the momentum: Culture shift across ISED
- Data Steward and Champion network established
- Implement & oversee data processes
Adopting a data culture: People value their data and treat it as an asset
- Monitor adoption of data processes & standards aligned with GoC
- Data Stewards facilitate access to data
Data Access
Laying the foundations: Data access challenges are well understood
- Inventory & evaluation of data assets
- Inventory data sharing agreements
- Assessment of legislative & policy framework for data sharing
Building the momentum: Work on transformative data access initiatives
- Develop common consent statement for data sharing
- Create roadmap for a data sharing hub
- Partner with Sectors to pilot data sharing and data integration Investigate data sharing opportunities across all levels of government
Adopting a data culture: ISED data are open by default
- Launch common consent statement for data sharing & monitor data sharing
- Deploy self-service data sharing hub
- Expand data sharing to all levels of government
Data Framework
Laying the foundations: Data framework and models are developed
- Data standards, including Common Business Profile and dictionaries, developed and piloted Framework for ethical, secure use & storage of data developed
- Detailed data models for collection, acquisition, processing and storage conceptualized and piloted
Building the momentum: Put in place data framework and models
- Process to handle and use data are known
- Quality assurance standards developed Data standards launched
- Framework for ethical & secure data use implemented
- Data models in place across the department
Adopting a data culture: Protection of data via privacy by design
- Staff confidently conduct work with high quality data, with well-established data standards, definitions, and the privacy and security of Canada's data assured
Talent
Laying the foundations: Baseline and identify skills gaps
- Identify business needs
- Assess data literacy
- Identify data-related learning and development
Building the momentum: Our workforce begins to transform
- Develop career path & data competencies
- Upskill and retrain new and existing staff
- Recruitment strategy based on required data skills
Adopting a data culture: We have trained people to reach our goals
- Ongoing recruitment & development
- Talent retention initiative
- Data as core competency for career development
Innovation
Laying the foundations: Foundation for change is established
- Early opportunities identified
- First data analytics pilots undertaken
- Success stories shared
Building the momentum: Experimentation begins to yield results
- Roll-out successful pilots to other sectors
- Continue to communicate approaches and use cases
- Identify mechanism for making decisions on proposed innovative solutions
Adopting a data culture: Innovation becomes common business practice
- Initiate departmental analytics support
- Develop Free Agent data talent matching service (data-skilled talent pool for short-term work)
- Establish data science pipeline
Technology
Laying the foundations: Higher organizational awareness of existing solutions
- Determine technology requirements
- Establish technology strategy
- Experiment with technology solutions for data (management, sharing, creation, data analytics)
- Roadmap for Client Relationship Management (CRM)
Building the momentum: New tools and processes put in place
- Implement technology strategy
- Business processes for use of new technologies
- On-site storage, common data software suite
- Business analytics tools available
Adopting a data culture: Internal technology keeps pace with innovation
- Integrated suite of IT tools for data and analytics
- Departmental Client Relationship Management with Common Business Profile
- Continual evaluation of Next Generation technology with new tech use on demand